Hey,
Thanks for visiting my blog.
In this article I’ll discuss about what is cybersecurity and its importance.
In today’s interconnected world, where our lives and businesses are increasingly reliant on digital technologies, cybersecurity has become a critical issue. With the growing sophistication of cyber threats, it is essential to understand the principles, practices, and technologies involved in safeguarding our systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, modification, or destruction. This comprehensive guide will delve into the realm of cybersecurity, providing insights into its significance, core principles, essential pillars, and the evolving landscape of cyber threats and defenses.
What is Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the practice of guarding systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, exposure, dislocation, revision, or destruction. It is a critical aspect of information security in today’s digital world, where sensitive information is increasingly stored and transmitted electronically.
Cybersecurity encompasses a wide range of practices, technologies, and policies designed to protect against cyber threats. These threats can come from a variety of sources, including malicious actors, criminal organizations, and nation-states.
The goals of cybersecurity are to:
- Protect Confidentiality: Ensure that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized users.
- Maintain Integrity: Ensure that data and systems are accurate and reliable.
- Ensure Availability: Ensure that systems and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed.
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires continuous vigilance and adaptation to new threats and vulnerabilities.
Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is crucial in today’s digital world due to its significant impact on individuals, businesses, and organizations. Here is a quick summary of its importance:
- Protecting Sensitive Information: Cybersecurity safeguards sensitive personal and business information, including financial data, intellectual property, and customer records. Breaches of this information can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
- Maintaining Business Continuity: Cyberattacks can disrupt business operations, causing downtime, revenue loss, and customer dissatisfaction. Cybersecurity measures help ensure business continuity by protecting systems and data from disruptions.
- Protecting Critical Infrastructure: Cybersecurity is essential for protecting critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, and financial markets. Cyberattacks on these systems can have devastating consequences for society.
- Compliance with Regulations: Businesses and organizations are increasingly subject to data privacy and cybersecurity regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. Cybersecurity measures help ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid potential fines and penalties.
- Protecting Individuals from Cyber Crime: Cybersecurity helps protect individuals from cyber crime, such as identity theft, phishing scams, and ransomware attacks. These crimes can cause financial loss, damage to creditworthiness, and emotional distress.
In summary, cybersecurity is not just a technical issue; it’s a business necessity and a societal imperative. By investing in cybersecurity measures, organizations can protect their assets, safeguard their reputation, and contribute to a safer digital world.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats are diverse and constantly evolving, aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and data to gain unauthorized access, disrupt operations, or steal sensitive information. These are a few typical categories of cybersecurity threats:
- Malware: Malware encompasses malicious software designed to harm systems or steal data. Ransomware, spyware, Trojan horses, worms, and viruses are among them.
- Phishing: Phishing attacks involve tricking users into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details, by sending deceptive emails or creating fake websites.
- Ransomware: Ransomware encrypts a victim’s files or systems, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. It can target individuals, businesses, and organizations.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) Attacks: DoS attacks aim to flood a system or network with traffic, overwhelming its resources and making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) Attacks: MitM attacks intercept communication between two parties, allowing the attacker to eavesdrop, modify, or block the data.
- Zero-day Attacks: Zero-day attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software or systems that are unknown to the vendor or developer, leaving no time for patching before attackers strike.
- SQL Injection: SQL injection attacks exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to inject malicious SQL code, allowing attackers to manipulate databases and steal data.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): XSS attacks inject malicious scripts into websites, allowing attackers to steal user cookies, redirect users to phishing sites, or execute further attacks.
- Password Attacks: Password attacks aim to crack or brute-force user passwords to gain unauthorized access to accounts and systems.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats arise when authorized users, such as employees, contractors, or privileged users, misuse their access to harm a company or steal sensitive information.
- Social Engineering: Techniques used to manipulate users into divulging confidential information or taking actions that compromise their security.
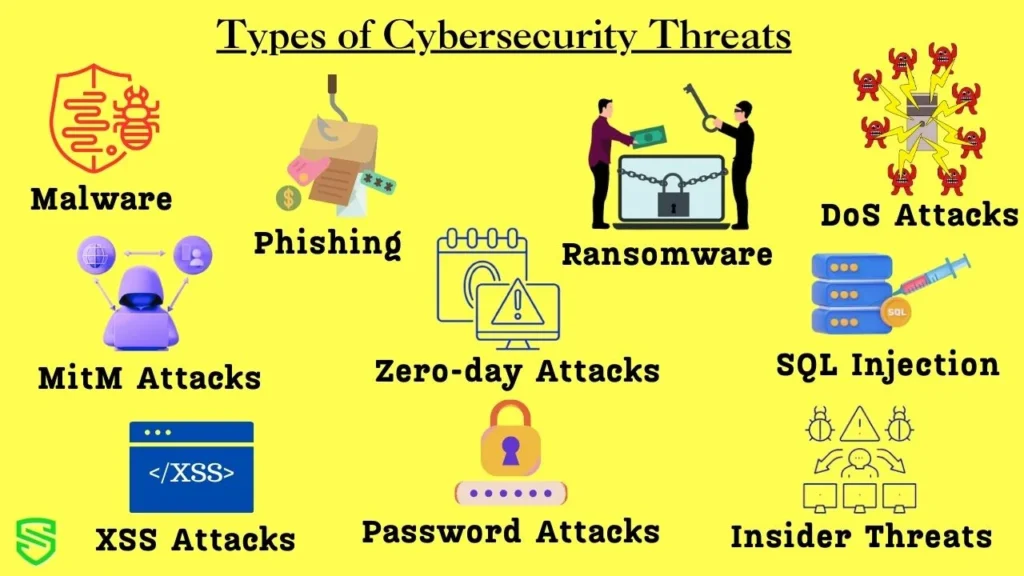
Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to individuals, businesses, and organizations, and it is crucial to implement robust security measures to protect against these attacks.
Impact of Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats have a far-reaching impact on individuals, businesses, and organizations. The following are some of the principal effects:
- Financial Losses: Cybersecurity breaches can lead to significant financial losses due to direct costs, such as ransom payments, data recovery expenses, and legal fees, as well as indirect costs, such as decreased sales, harm to one’s reputation, and client attrition.
- Data Breaches and Privacy Violations: Cybersecurity breaches can expose sensitive personal or business information, leading to identity theft, fraud, and damage to reputation. Individuals may experience emotional distress, financial hardship, and difficulty restoring their creditworthiness.
- Disruptions to Operations and Services: Cyberattacks can disrupt business operations, causing downtime, loss of productivity, and reduced customer satisfaction. In critical infrastructure sectors, disruptions can have cascading effects on society, such as power outages, transportation disruptions, and financial market instability.
- Reputational Damage: Cybersecurity breaches can severely damage an organization’s reputation, eroding customer trust, weakening brand value, and making it difficult to attract and retain talent.
- Legal Liabilities and Regulatory Compliance: Cybersecurity breaches may lead to legal liabilities and regulatory non-compliance, resulting in fines, penalties, and lawsuits. Organizations may face increased scrutiny from regulators and potential consumer lawsuits.
- Threats to National Security: Cybersecurity threats can target critical infrastructure, government systems, and sensitive national security information. Cyberattacks on these systems can have severe consequences for national security, disrupting essential services and compromising sensitive data.
The impact of cybersecurity threats is not limited to large corporations or government agencies. Individuals, small businesses, and non-profit organizations are also vulnerable to cyberattacks, with potentially devastating consequences. It is crucial for everyone to take cybersecurity seriously and implement appropriate measures to protect themselves and their organizations.
Evolution of Cybersecurity
The evolution of cybersecurity has been shaped by the ever-changing technological landscape and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats.
A. Early Days of Cybersecurity
1. Early computer and data security
- 1960’s and 1970’s: The early days of cybersecurity focused on physical security measures, such as locking up computer rooms and securing access to terminals.
- 1980’s: The Morris Worm, the first widely distributed computer virus, highlighted the vulnerability of interconnected systems.
- 1990’s: The rise of the Internet and e-commerce led to an increase in cyberattacks, such as phishing and malware.
2. Maturity and Professionalization
- 2000’s: Cybersecurity became a recognized profession with the establishment of organizations like the International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium (ISC)² and the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA).
- 2010’s: The Stuxnet worm, targeting Iran’s nuclear program, demonstrated the potential of cyberattacks to disrupt critical infrastructure.
- 2020’s: Cybersecurity has become a global concern with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the growing attack surface due to the Internet of Things (IoT) and Cloud Computing.
B. Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to automate threat detection, anomaly analysis, and incident response.
- Zero-trust security is gaining traction, emphasizing continuous verification of user identities and access privileges.
- Data security is becoming increasingly important as organizations store and process vast amounts of sensitive data in cloud environments.
C. The Future of Cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity will remain a critical issue as technology continues to evolve and cyber threats become more sophisticated.
- Organizations will need to adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, integrating it into their overall risk management strategies.
- Cybersecurity professionals will play an increasingly important role in protecting organizations from cyber threats and ensuring the resilience of critical infrastructure.
Conclusion Cybersecurity has evolved from a niche concern to a global imperative. As technology continues to advance and cyber threats become more sophisticated, organizations and individuals must remain vigilant and adopt robust cybersecurity practices to protect their data, systems, and privacy.
Core Principles of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is built upon three fundamental principles that form the foundation of protecting information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. These principles are:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information. This principle involves implementing controls to restrict access to sensitive data and systems, such as user authentication, access controls, and data encryption.
- Integrity: Preserving the reliability and correctness of systems and data. This principle involves protecting data from unauthorized modification or corruption, ensuring that systems function as intended, and safeguarding against tampering or manipulation.
- Availability: Ensuring that systems and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed. This principle involves protecting against outages, disruptions, and denial-of-service attacks that could prevent authorized users from accessing critical systems or data.
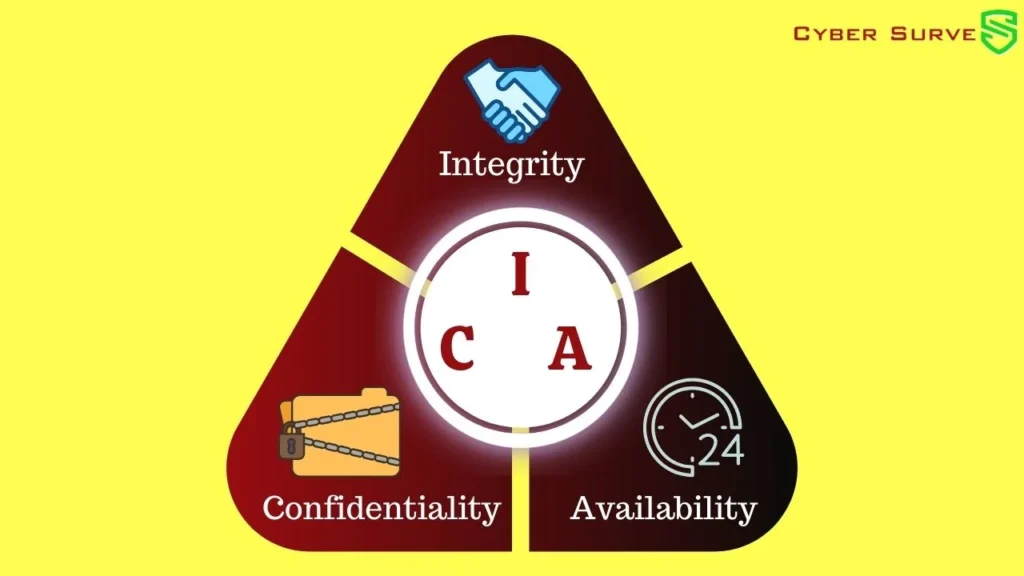
These three principles are interconnected and interdependent. For instance, maintaining confidentiality helps protect the integrity of data by ensuring that only authorized users can access and modify it. Similarly, ensuring availability is crucial for maintaining confidentiality and integrity, as unauthorized access or data corruption can disrupt or compromise critical systems.
By adhering to these core principles, organizations and individuals can significantly reduce their cybersecurity risks and safeguard their valuable information and systems.
Pillars of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity encompasses a wide range of practices, technologies, and policies designed to protect against cyber threats. These efforts can be categorized into five key pillars:
- Network Security: This pillar focuses on protecting network infrastructure from unauthorized access, eavesdropping, and attacks that could disrupt network traffic or compromise data in transit. It involves implementing network security devices like firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and network segmentation strategies.
- Application Security: This pillar focuses on securing applications from vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access, manipulate data, or compromise the application’s functionality. It involves secure coding practices, input validation, vulnerability scanning, and application testing methodologies.
- Endpoint Security: This pillar focuses on protecting endpoints, such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices, from malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access. It involves endpoint protection software, anti-virus and anti-malware solutions, device management policies, and user education programs.
- Data Security: This pillar focuses on protecting data at rest and in transit from unauthorized access, modification, or disclosure. It involves data encryption, access controls, data loss prevention (DLP) solutions, and data classification and labeling practices.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): This pillar focuses on managing user identities, access permissions, and authentication processes to prevent unauthorized access and insider threats. It involves user authentication mechanisms, role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and identity and access governance (IAG) frameworks.
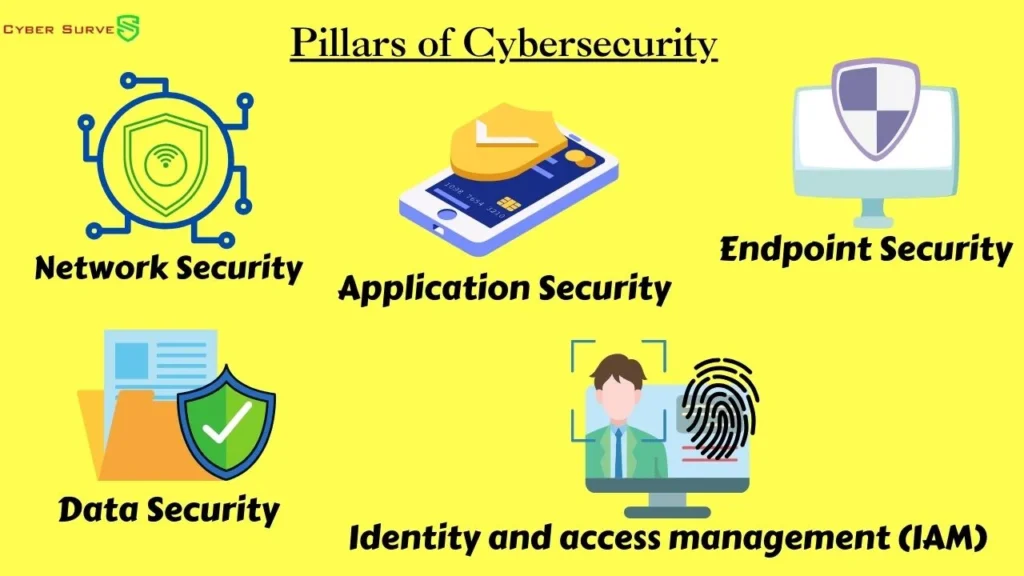
These five pillars form the foundation of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By addressing each pillar, organizations can significantly reduce their cybersecurity risks and protect their valuable information and systems.
Cybersecurity Practices and Technologies
Cybersecurity practices and technologies are the tools and strategies employed to safeguard systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. These practices and technologies encompass a wide range of measures, from basic user awareness training to sophisticated encryption algorithms and firewalls.
A. Common Cybersecurity Practices:
- Password Management: Enforcing strong password policies, encouraging the use of password managers, and employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhance password security.
- User Awareness Training: Educating employees about cyber threats, phishing scams, and safe online practices reduces the risk of human error and social engineering attacks.
- Software Updates and Patch Management: Promptly applying software updates and security patches eliminates known vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
- Access Controls and Privileged Access Management: Implementing access control mechanisms restricts user access to sensitive data and systems based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit protects it from unauthorized access, even if it falls into the wrong hands.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Firewalls act as barriers between trusted and entrusted networks, while IDS/IPS monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and potential attacks.
- Anti-virus and Anti-malware Software: Installing and regularly updating anti-virus and anti-malware solutions provides protection against malicious software and zero-day attacks.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regular data backups ensure the ability to restore critical information in the event of a cyberattack or system failure.
B. Emerging Cybersecurity Technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are being employed to detect anomalies in network traffic, identify suspicious user behavior, and predict potential cyberattacks.
- Zero-trust Security: Zero-trust security architecture assumes that no user or device can be trusted implicitly and requires continuous verification of access permissions and identity.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions prevent sensitive data from being ex-filtrated from the organization by monitoring and controlling data transfers.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide real-time visibility into endpoint activity, enabling rapid detection and remediation of cyberattacks.
- Bio-metric Authentication: Bio-metric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanners and facial recognition, provide a more secure and convenient alternative to traditional passwords.
By implementing a combination of these cybersecurity practices and technologies, organizations can significantly strengthen their defenses against cyber threats and protect their valuable assets.
Cybersecurity Challenges and Trends
A. Cybersecurity Challenges
Cybersecurity challenges are constantly evolving as attackers develop new techniques and exploit emerging technologies. Some of the key challenges facing organizations today include:
- Increasing Sophistication of Cyber Attacks: Attackers are becoming more sophisticated in their methods, using advanced persistent threats (APTs) and zero-day exploits to target critical systems and data.
- Growing Attack Surface: The expanding attack surface due to the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and mobile devices poses significant challenges in securing these interconnected devices and networks.
- Evolving Cybersecurity Regulations and Compliance: Organizations must adhere to a growing body of cybersecurity regulations and compliance requirements, which can be complex and costly to implement.
- Cybersecurity Skills Gap: The demand for cybersecurity professionals far exceeds the available supply, creating a skills gap that makes it difficult for organizations to find and retain qualified talent.
B. Cybersecurity Trends
Several trends are shaping the future of cybersecurity, including:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): AI and ML are being applied to automate threat detection, anomaly analysis, and incident response, improving the ability to identify and respond to cyberattacks.
- Zero-trust Security: Zero-trust security is gaining traction as organizations move away from traditional perimeter-based security models, adopting a more granular approach to access control and identity verification.
- Data Security in a Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environment: Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud environments, creating challenges in securing data across multiple cloud platforms and providers.
- Cybersecurity Awareness and Education: Cybersecurity awareness and education are becoming increasingly important as the attack surface expands and user behavior plays a critical role in preventing cyberattacks.
- Global Cybersecurity Cooperation and Collaboration: International cooperation and collaboration are essential for addressing global cybersecurity threats and sharing threat intelligence among nations and organizations.
In addition to these trends, the future of cybersecurity is also likely to be shaped by emerging technologies, such as Blockchain and Quantum Computing. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we secure our systems and networks, but they also pose new challenges.
Organizations will need to stay abreast of these trends and technologies in order to effectively protect themselves from cyberattacks. They will also need to adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, integrating it into their overall risk management strategies.
Here are some specific examples of how AI and ML can be used in cybersecurity:
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: AI algorithms can be used to analyze network traffic, log data, and other security telemetry to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a cyberattack.
- ML-Based Anomaly Analysis: ML models can be trained to identify suspicious activity in user behavior, such as accessing unauthorized data or making unusual network requests.
- Automated Incident Response: AI-driven systems can automate the response to cyberattacks, such as isolating infected systems, blocking malicious traffic, and notifying security teams.
- Predictive Threat Modeling: AI algorithms can be used to analyze historical data and identify trends that may indicate future cyberattacks.
- Adaptive Security: AI-powered systems can continuously learn and adapt to new threats, providing more effective protection against evolving cyberattacks.
By leveraging AI and ML, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity capabilities and better protect their valuable assets from cyberattacks.
Conclusion: What is Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a complex and ever-evolving field, but it is essential for protecting our digital assets and safeguarding our privacy. Organizations and individuals alike must adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, staying informed about the latest threats, implementing robust security measures, and practicing good security habits. By working together and leveraging the latest technologies, we can build a more resilient and secure digital world.
FAQs
Thank You
I hope this article is of interest to you and that you are doing well. If so, please leave a comment and tell your friends and colleagues.


Pingback: Why Cloud Security Is Important For An Organization - Cyber Surve
Pingback: A Guide to Information Security for Beginners 2024 - Cyber Surve
Pingback: What are The 3 Elements of Network Security? - Cyber Surve
Pingback: How Does Mobile Security Work in 2025? -
Pingback: How to Learn Web Application Security: A Step-by-Step Guide
Pingback: How I Passed the ISC2 Certified in Cybersecurity Certification Exam 2025