What are The 3 Elements of Network Security?
Network security protects systems, devices, apps, and digital infrastructure from internet attacks. It encompasses a wide range of hardware and software products as well as procedures used to safeguard computing networks’ confidentiality, integrity and availability.
Network security is generally considered to be a subfield of cybersecurity. Network security is one of the primary aspects of cybersecurity since the internet’s interconnectedness is the primary source of security threats.
This blog post focuses closely on network security, highlighting its importance, and What are The 3 Elements of Network Security?
Introduction to Network Security
A. What is Network Security
Network security encompasses the policies, procedures, and technologies implemented to protect a network infrastructure from unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of service. It aims to create a secure environment where data remains confidential, integrity is preserved, and systems operate without disruption.
B. Importance of Network Security
Network security is a really big deal these days. Think about all the important stuff that gets sent over computer networks – things like your bank account details, private emails, company secrets and more. Without proper security, hackers could break in and access that sensitive information or mess with critical systems.
That’s why having a secure network locked down with firewalls, encryption, and other protective measures is crucial. It’s like having a really tough lock on your front door to keep the bad guys out. Good network security protects your valuable data from being stolen or misused by cybercriminals.
It also helps businesses stay up and running smoothly without costly interruptions from hacker attacks or virus outbreaks grinding everything to a halt. Plus, many industries have laws requiring a certain level of data security, so robust network security helps companies avoid hefty fines.
But it’s not just about money – network breaches can severely damage a company’s reputation and erode customer trust when private info gets exposed. Proper security gives people peace of mind.
So in our connected world with remote workers and smart gadgets everywhere, keeping your network locked down tight is just good common sense. It’s the best way to protect your digital life from the shadier elements out there.
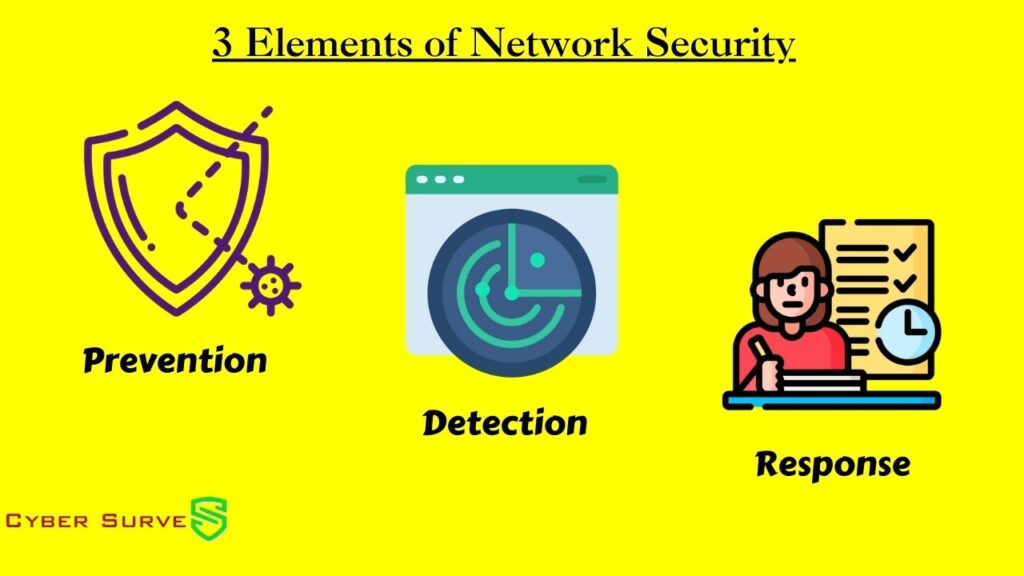
I. What are The 3 Elements of Network Security
Three essential components form the foundation of every strong network security strategy: Prevention, Detection, and Response.
1. Prevention
Prevention is all about putting up tough barriers to block the bad guys before they can even get into your networks in the first place. It’s like building a solid perimeter fence around your property.
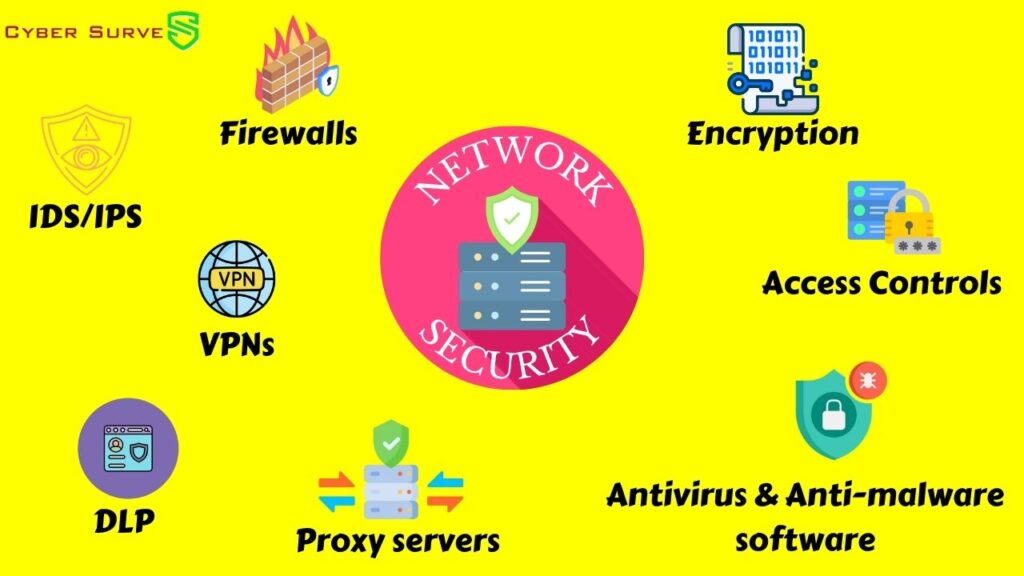
- Firewalls: One of the biggest preventive tools is firewalls. These act like super bouncy bouncers at the entrance, checking everyone’s ID and only letting in folks that meet the strict security rules you’ve set up. They filter all the incoming and outgoing internet traffic to keep unauthorized people and dodgy stuff out.
- Access control: Access control is another huge part of prevention. It’s like having a very picky doorman who makes everyone go through a bunch of checks – fingerprint scans, password entries, security questions, you name it – before they’re allowed inside. This multi-factor authentication helps ensure only legit users can access important systems and data.
- Vulnerability Management: You also want to be on top of patching up any security holes or vulnerabilities that hackers could try to slip through, just like fixing any cracks or weak spots in your home’s exterior doors and windows. Regular updates and vulnerability management is key.
- Network Segmentation: It also helps to segment your networks into smaller neighborhoods with limited access between them. That way, if one area gets invaded, the intruder can’t just run free through the whole place.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption is like spinning all your top-secret messages into secret code before sending them out. So even if a shady person intercepts the messages, they just see nonsense without the decryption key.
- Security Awareness Training: Finally, training your friends and coworkers on security best practices empowers everyone to be extra watchful for potential threats like phishing scams or other social engineering tricks aimed at tricking people.
2. Detection
No matter how solid your preventive defenses are, some sneaky cyber threats might still find a way to slip through the cracks. That’s why having a good detection system is so important – it’s like having security cameras and motion sensors keeping watchful eyes and ears out for any sketchy activity.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): One of the main detection tools is called an intrusion detection/prevention system (IDS/IPS). This bad boy constantly monitors all the internet traffic flowing in and out of your networks. It’s trained to recognize patterns and behaviors that seem out of the ordinary or malicious, kind of like a security guard who can spot a suspicious person. When it detects a potential threat, it sounds the alarm and can even automatically block the attack.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Another big part of detection is the SIEM system – that’s a central command center that collects and analyzes security data from all your different defensive tools like firewalls, antivirus, etc. It pieces together a complete picture so security staff can easily spot any concerning events happening across your networks.
- Log Monitoring: Speaking of security staff, they also keep close watch on system logs from devices, servers and applications running on the network. These logs record all traffic and activity, so going through them regularly helps trained admins identify anything unusual that could be a sign of intrusion or compromise.
3. Response
Even with the best preventive defenses and watchful detection systems, sometimes hackers or cybercriminals may still find a way to infiltrate your networks. That’s why having a clear game plan for responding to security incidents is so crucial. It’s like having a fire evacuation plan for your home or workplace – you hope you never need to use it, but if an emergency does strike, you’re prepared to minimize the damage and get things back to normal quickly.
- Incident Identification and Containment: The first step is identifying that a breach has occurred and trying to contain it fast. It’s like putting out the fire before it spreads further. You may need to isolate and cut off access to the impacted systems or servers before hackers can wreak more havoc.
- Investigation and Eradication: Next up is the investigation phase – calling in the cybersecurity experts to do some digital forensics work and figure out what exactly happened, how severe the intrusion was, and where it originated from. Think expert fire inspectors meticulously examining the scene. Once they identify the vulnerabilities that were exploited, they can start eradicating the threat by removing any malware, closing security holes, and regaining control of infiltrated systems.
- Recovery: With the fire now extinguished, it’s time for recovery efforts focused on restoring affected data, applications and services back to full operational health as fast as possible. Having reliable backups is key here, just like having blueprints helps rebuild after fires.
- Reporting and Learning: Finally, there’s the reporting and learning phase where the incident gets thoroughly documented. It’s about taking lessons from this experience on where your security failed, then using those insights to improve response plans and beef up preventive measures against future attacks. It helps get your cyber defenses blazing again, stronger than before.
Having an actionable incident response strategy covering all those bases is vital for minimizing the disruption and damage caused by any successful cyberattack that slips through the cracks. Just like any emergency preparedness plan – you’ll be relieved you invested the effort if you ever need to execute it for real.
II. Threats to Network Security
A. Common Types of Threats
- Malware Attacks
Malware, which includes viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware, is a major threat to network security. These malicious programs can infect systems, steal data, or cause systems to malfunction.
- Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing attempts try to trick users into giving away sensitive information or doing things that compromise security. This is often done through fake emails, messages, or websites. Social engineering tactics take advantage of human psychology to manipulate people into revealing confidential information or performing unauthorized actions.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks try to disrupt network services by overwhelming servers or network resources with too much traffic, making them unavailable to legitimate users.
B. Vulnerabilities in Networks
- Weak Passwords
Weak or easily guessable passwords are a significant security risk, as attackers can exploit them to gain unauthorized access to network resources.
- Unsecured Devices
Unsecured devices, such as IoT devices or unpatched computers, can provide entry points for attackers or be used to launch attacks against the network.
- Lack of Encryption
Failure to encrypt sensitive data while it’s being transmitted or stored makes it vulnerable to being intercepted or accessed without authorization, increasing the risk of data breaches.
C. Consequences of a Breach
- Data Theft and Privacy Issues
Breaches can result in the theft or exposure of sensitive data, leading to privacy violations, identity theft, or non-compliance with regulations.
- Financial Losses
The financial impact of a breach can be significant, including direct costs for responding to the incident, legal fees, regulatory fines, and indirect costs like losing customers and damage to the brand’s reputation.
- Reputational Damage
A breach can erode trust and credibility, tarnishing an organization’s reputation and potentially leading to long-term negative effects on its business operations.
III. Technologies for Network Security
A. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
- Detecting Suspicious Activities
IDS/IPS solutions analyze network traffic patterns and behavior to identify anomalies or known attack signatures that indicate malicious activity.
- Blocking Intrusions
When a threat is detected, IDS/IPS systems can take automated action to block or mitigate the attack, preventing further harm to the network.
- Benefits of IDS/IPS
IDS/IPS solutions provide real-time threat detection and response capabilities, helping organizations proactively defend against a wide range of cyber threats.
B. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- Securing Remote Connections
VPNs encrypt network traffic between remote users and the corporate network, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity over untrusted networks.
- Encryption in VPNs
VPNs use encryption protocols to scramble data transmitted between the client and server, making it unreadable to eavesdroppers or attackers.
- Advantages of VPNs
VPNs enable secure remote access to corporate resources, facilitate secure communication between distributed teams, and protect sensitive data from being intercepted or tampered with.
C. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Centralized Monitoring
SIEM solutions collect and correlate security event logs from across the network, providing a centralized view of security-related activities and threats.
- Analyzing Security Events
SIEM platforms use advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate security incidents.
- Enhancing Incident Response
By providing real-time alerts and actionable insights, SIEM solutions empower organizations to respond promptly to security incidents and mitigate potential risks.
IV. Best Practices for Network Security
A. Educating Employees
- Importance of Cybersecurity Training
Regular cybersecurity training programs raise awareness among employees about the latest threats, best practices for secure behavior, and the importance of following security policies.
- Raising Awareness on Phishing
Training sessions on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts help employees identify suspicious emails, links, or attachments, reducing the risk of falling victim to social engineering attacks.
- Creating a Security-Conscious Culture
Fostering a culture of security consciousness encourages employees to take ownership of their role in maintaining a secure work environment, promoting collaboration and vigilance against potential threats.
B. Establishing Incident Response Plans
- Formulating Response Teams
Designating roles and responsibilities within an incident response team ensures a coordinated and effective response to security incidents, minimizing the impact on business operations.
- Conducting Regular Drills
Simulating security incidents through tabletop exercises or penetration testing helps organizations evaluate the effectiveness of their incident response plans and identify areas for improvement.
- Learning from Past Incidents
Post-incident reviews and analysis provide valuable insights into the root causes of security breaches, enabling organizations to implement corrective actions and strengthen their security posture.
C. Regular Audits and Compliance Checks
- Compliance Standards in Network Security
Regular audits and compliance checks ensure that organizations adhere to industry regulations and best practices for network security, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties or legal consequences.
- Auditing Networks for Vulnerabilities
Vulnerability assessments and penetration testing identify weaknesses within the network infrastructure, allowing organizations to prioritize remediation efforts and mitigate potential risks.
- Adhering to Data Regulation
Compliance with data protection laws and regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, ensures that sensitive information is handled and stored securely, minimizing the risk of data breaches and regulatory fines.
V. Network Security Solutions for Different Needs
- For Small Businesses: Affordable and easy-to-use security solutions tailored to the specific needs and budget constraints of small businesses, such as unified threat management (UTM) devices or cloud-based security services.
- For Enterprises: Scalable and integrated security platforms that provide comprehensive protection across diverse IT environments, including advanced threat detection, endpoint security, and network segmentation capabilities.
- For Cloud Environments: Cloud-native security solutions designed to protect cloud workloads, applications, and data from emerging threats, ensuring compliance and data privacy in dynamic and distributed cloud environments.
VI. Conclusion
In today’s highly connected world, network security is a critical necessity for organizations of all sizes and industries. By taking a proactive approach to network security, implementing robust preventive measures, and fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can strengthen their defenses against evolving cyber threats and safeguard their most valuable assets.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Thank You
I hope this article is of interest to you and that you are doing well. If so, please leave a comment and tell your friends and colleagues.